Webinar
Antibody validation: innovative staining solutions to support your antibody validation process
Posted on:
Why is antibody validation important?
Antibodies are one of the most important reagents in basic, translational and clinical research. They are fundamental detection tools, used in a variety of applications to identify protein expression. However, the quality and validation thoroughness of antibodies can substantially vary, having led to false findings in the past1. As many as 50% of commercially available antibodies fail to perform as expected in their intended applications2. Unfortunately, significant resources have been poorly invested in experiments that led to misleading conclusions. Antibodies are to blame as a key contributor to the “reproducibility crisis” 3.
Reproducibility is a cornerstone of scientific progress. For this reason, the International Group for Antibody Validation (IWGAV) was formed with the goal of setting standarized guidelines for the antibody validation process4 to establish the foundation for reproducible antibody-based assays.
What are the antibody validation principles?
“Validation is the experimental proof and documentation that a specific antibody is suitable for an intended application or purpose”5. The IWGAV established the following pillars to verify antibody specificity:
- Genetic validation: expression of the target protein is decreased or eliminated through siRNA/CRISPR-Cas9 mediated approaches.
- Orthogonal validation: assessment of the target protein abundance through a correlation between an antibody-independent (such as qPCR, RNAseq, or mass spectrometry) and antibody-dependent strategy.
- Independent antibody validation: correlation between data generated using multiple antibodies with non-overlapping epitopes to the target of interest.
- Tagged-protein expression validation: comparison of the data generated using an antibody directed at the protein of interest versus an antibody directed at the tagged target protein.
- Immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry validation (IP-MS): mass spectrometry analysis of the peptide sequences captured by the antibody via immunoprecipitation.
The presented pillars provide evidence that an antibody binds to the intended target and allows for cross-reactivity assessment under the evaluated conditions4.
Validating an antibody for immunohistochemistry (IHC), step by step
Confirming that an antibody works as intended under your own experimental setting is crucial for the validity of results. To validate an antibody for IHC, there are certain recommended steps to follow before moving on to the validation pillars6,7.
Firstly, researchers should look at the sub-cellular localization of the protein of interest. This will show if the localization of expression takes place as expected. The robustness of the antibody staining can be assessed by looking at its performance across a wide range of tissue types (Figure 1).
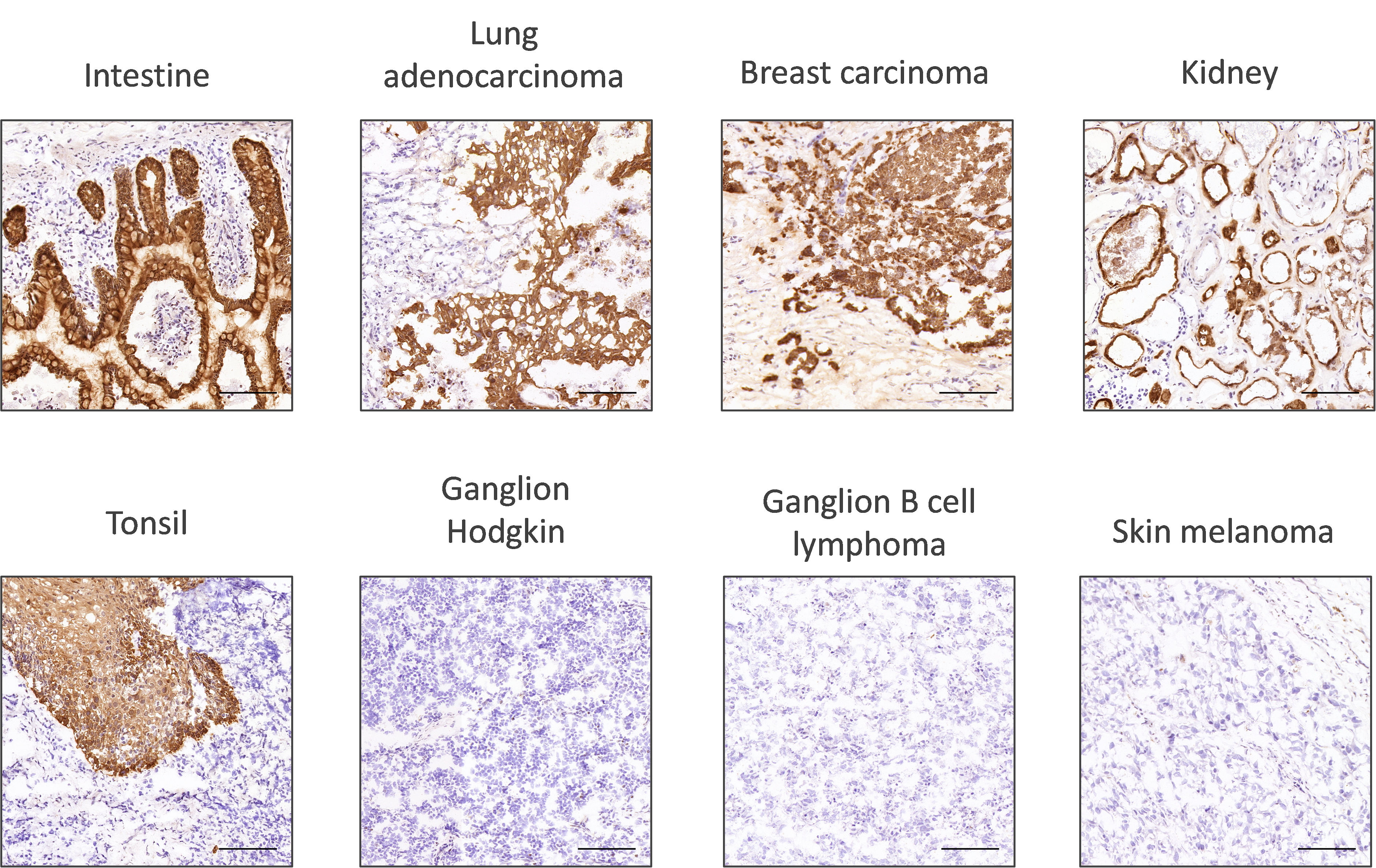
Secondly, to ensure that the selected validation pillars are carried out in the best possible conditions, it is essential to optimize the antigen retrieval step, the antibody concentration, and reagent incubation times6.
The validation process is therefore lengthy and requires multiple steps. This can also have an impact on data reproducibility due to a significant number of manual, error-prone optimizations.
Speed up your assay validation process
Antibody validation can be time-consuming, but it is essential for quality data generation. Thanks to next-generation technology innovations, it is now possible to optimize conditions for multiple antibodies quickly, without compromising on data quality and reproducibility, by utilizing a novel microfluidic chip, which offers significant advantages in antibody validation workflows:
Related Articles
HORIZON™ drives insights into the glioblastoma tumor microenvironment
Posted on 27 Aug 2025
Read Post