Spatial Biology Education
Marker-informed cell segmentation with HORIZON™
Posted on:

Cell segmentation is a crucial step in multiplex image analysis, designed to precisely delineate the boundaries of single cells (Figure 1).
Multiomics (proteomics & transcriptomics) signal quantification quality depends on cell segmentation quality. Cell segmentation inaccuracies may lead to incorrect signal assignment and bleed-through (crosstalk) which can in turn result in false positive detections and errors in phenotype assignment. Recent advancements in image analysis enable taking advantage of protein expression to delineate cell boundaries. However, there is no single marker to delineate all cell types reliably. The problem is further complicated by the diversity of cell types across different tissue types and species. To tackle these limitations, HORIZON™ incorporates a state-of-the-art marker-based cell segmentation approach, which allows mixing the signal from multiple channels together to achieve high-quality cell segmentation across different cell types.
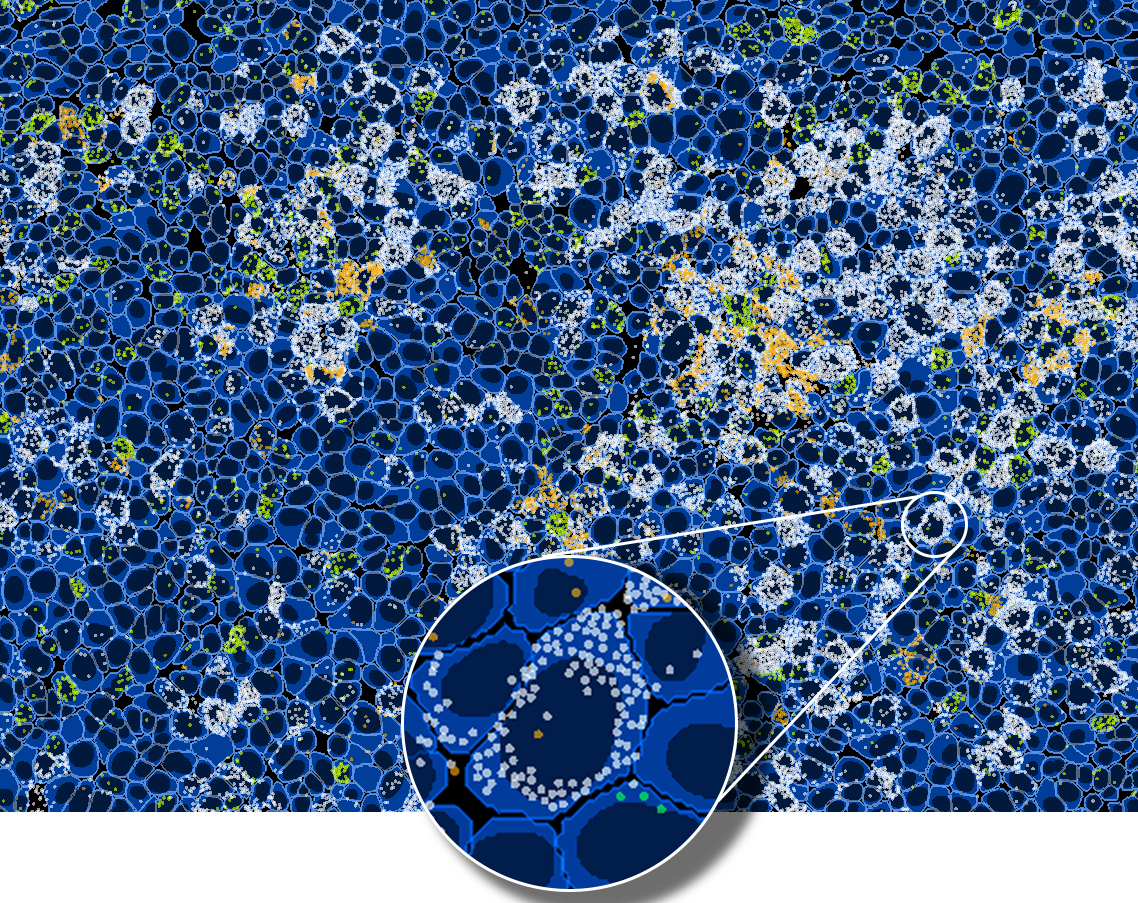
HORIZON™ workflow

Thanks to the seamless HORIZON™ and COMET™ integration, the image analysis workflow starts directly after image acquisition and takes advantage of deep-learning algorithms optimized using COMET™ data. Cell segmentation primarily benefits from automatic autofluorescence subtraction, which can be executed in a few clicks to improve image contrast significantly. You can choose multiple markers to perform cell segmentation, allowing them to segment different cell types simultaneously. HORIZON™ uses a state-of-the-art deep learning-based cell segmentation algorithm based on the InstanSeg approach [2]. It intelligently combines multiple channels to achieve superior segmentation results. The cell segmentation step is followed by feature extraction and classification steps that are crucial for downstream analysis.