Spatial Biology Education
DAPI’s crucial role in multiplex immunofluorescence
Posted on:
In cellular biology, DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) stands out as a critical fluorescent nuclear stain. It specifically targets the minor groove of double-stranded DNA, with a preference for adenine-thymine clusters1. The use of DAPI in multiplex immunofluorescence has revolutionized our understanding of cellular structures and functions, significantly propelling research forward across a wide range of scientific areas.
DAPI in multiplex immunofluorescence: more than just a nuclear marker
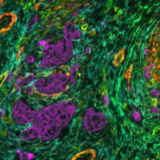
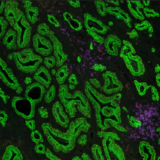
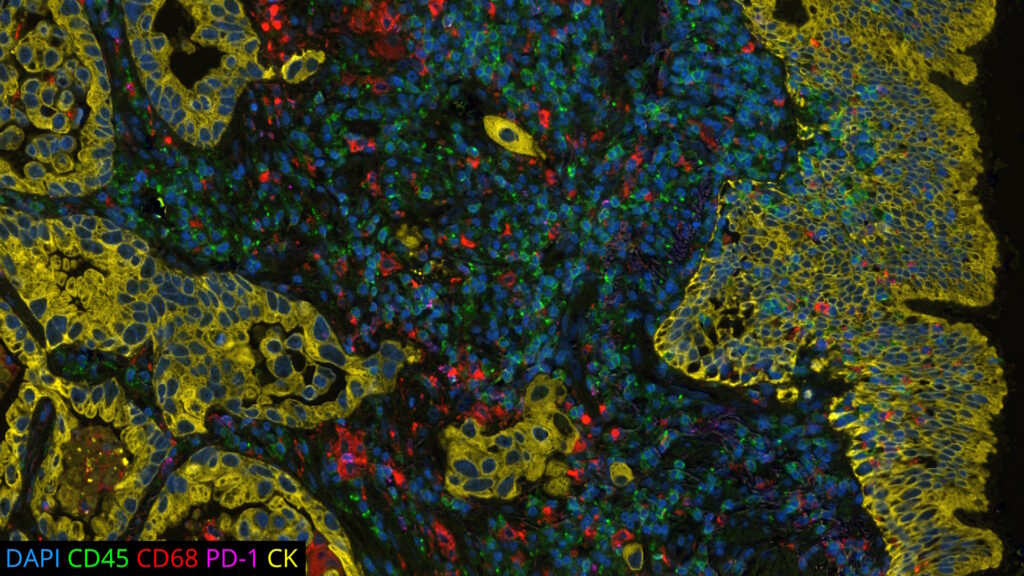
DAPI’s specific affinity for DNA renders it ideal for identifying and counting cells in mixed populations, a common scenario in complex tissue samples or cell mixtures. As a reliable nuclear counterstain, DAPI provides a crucial reference point for cell identification within a sample, as depicted in Figure 1. This is especially vital in cancer research and neuroscience studies, where cell populations often exhibit unique nuclear characteristics. Moreover, DAPI serves as a high-contrast stain, enhancing the delineation of nuclear boundaries.
Using DAPI in sequential immunofluorescence technology (seqIF™)
After understanding DAPI’s foundational role as a nuclear marker, we focus on its integration into seqIF™, comprising successive cycles of staining, imaging, and elution, as outlined in Figure 2. In the staining step, DAPI is critical as a counterstaining agent, aiding nuclear detection. During imaging, each marker, including DAPI, is allocated a dedicated microscope channel. This step is crucial for capturing detailed images without sample manipulation or user intervention. The images acquired at each cycle are stacked to create a multi-layer image where all the acquired biomarkers can be visualized together on the sample. Thanks to the constant DAPI stain at each cycle, images can be accurately aligned before registration. Finally, the gentle elution step efficiently removes antibodies while maintaining epitope stability and tissue morphology. You can learn more about elution efficiency and epitope stability with COMET™ in this Technical Note.